Secure QR Code: What is it and how can it be useful?

QR codes have been around for 30 years – yes, 30 years! They were invented by a Japanese company called DENSO in 1994. A form of two-dimensional barcodes, QR Codes today are used for a variety of purposes – from contactless payments to conveying information such as website addresses, contact information, and other information used in ticketing and boarding passes, quickly and easily.
Fun fact: ‘QR’ stands for ‘Quick Response’
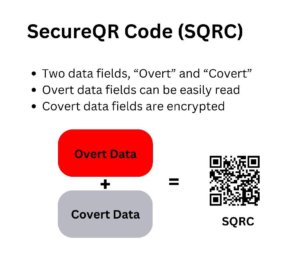
SecureQR code is a relatively new type of QR code which allows for two types of information to be encoded in one QR code – public and private. A Secure QR code (SQRC) looks just like a normal QR code, and the public information on that QR code will be readable just as a normal QR code. The private information is encrypted and only readable by authorised hardware and software with the appropriate decryption keys.
In order to generate an SQRC, the registered client application sends the information to the server which generates and returns the SQRC to the requesting application.
Decryption of the private information in an SQRC can be done by
- Authorised clients possessing the decryption key on authorised hardware. This option does not require internet connectivity.
OR - Authorised clients on any hardware (e.g. smartphones) sending the SQRC to the SQRC server. This option requires internet connectivity.
 Fig. 1 – Unauthorised client app only sees the public information in an SQRC
Fig. 1 – Unauthorised client app only sees the public information in an SQRC
 Fig. 2 – Authorised client app is able to read the private information in an SQRC
Fig. 2 – Authorised client app is able to read the private information in an SQRC
The private information encrypted in an SQRC is not stored in any database anywhere, it resides in an encrypted form on the QR code. This brings many benefits in terms of privacy and data security, as personal information can be stored on the QR code and carried by the user themselves.
One application of SQRC is the use of wristbands for patients in a healthcare setting. Here the QR codes can be used to store information specific to the patient, such as blood type, medical history, allergies, etc. This makes the information available at the point at which it is read, without requiring such information to be stored on a networked database.
Another application is where the SQRC is used to store facial recognition information in a digital identity application. The user presenting the SQRC can be required to pass a facial recognition check to verify their identity. As the SQRC can only be generated by authorised clients, the authenticity of the information on the SQRC can be verified; the identity of the user can therefore be verified by performing a facial recognition identification that is based on the biometric information on the SQRC.
As can be seen, SQRC opens up a world of possibilities and can be useful in solving a wide range of business problems. If you are interested in SQRC and would like to know more, do get in touch!